R020 File/Pipe Adapter
Outline
The File/Pipe adapter reads data from filesystem objects. The received data is forwarded to a configurable reader. Scripts are used to activate the streaming environment (stimulation). The adapter can be combined with other adapters using a multi-adapter port.
| Platforms |
|
|||
| Requirements |
|
|||
| Known limitations |
|
|||
| Status |
|
|||
| Operations |
|
|||
| Parameters: |
|
Video
Modes
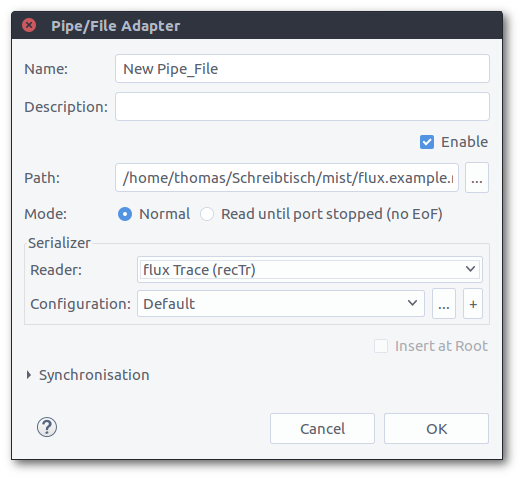
- In "Normal" mode, the adapter tries to open the file or pipe and reads its content until it receives an end-of-file notification.
- If "Read until port stopped" is chosen, the adapter ignores an end-of-file. This mode can be used if a process writes into the file while reading and no pipe is used (Windows does not support simple pipes).
Source Configuration
- Path: Use the button to open the file dialog.
Serializer
Configure the serializer by selecting a reader and optionally a reader configuration (some reader require a configuration, e.g. the CSV reader).You may use the buttons '+' and '...' to add and manage existing reader configurations (Preferences).
You may use the "Test Line Reader" (extracts lines from the raw input) and "Test Block Reader" (extract fixed size byte blocks) for debugging purpose.
Synchronization
Using a multi adapter port, you can combine an unlimited number of different input adapters. The synchronization section of the adapters allows you to synchronize inputs with different domain bases (e.g. each input has its own time base).
11 SynchronisationStimulation
There may be cases where the environment need to be stimulated to make the source data available. In this case, enable the "Enable Script" check and extend the stimulation script according to your needs.
The script is executed after connecting (background thread).
// file: java.io.File
// log: java.io.OutputStream,
// progress: progress control of type IPortProgress
// console: console output of type MessageConsoleStream
java.lang.Thread.sleep(100);
console.println("waited for"+file.getName());
doWhatever();
 32/64bit
32/64bit 32/64bit
32/64bit 32/64bit
32/64bit