R033 Member Extract Production
Outline
Extracts a member of a struct or an array, identified by the member name or id/index and creates a new signal of a given signal type.
| Platforms: |
|
|||
| Requirements: |
|
|||
| Known limitations: |
|
|||
| Status: |
|
|||
| Input signals: |
|
|||
| Output signal: |
|
|||
| Parameters: |
|
|||
| Operation: |
Input Signal Configuration
The production accepts 1 Array (IntegerArray,EventArray,FloatArray,TextArray) or Struct signal.
- Primary Source
- The primary source is the first source signal of the production.
Output Signal Configuration
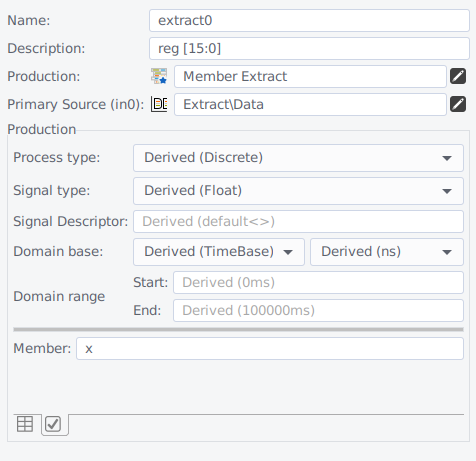
Productions are executed on the fly, as soon as the signal data is required for further processing, and re-executed when settings or input signal have been changed. Before executing a production, the system needs to know the source signals, the type and the domain of the signal. All these informations need to be entered into the plot configuration dialog. If you leave the configuration fields empty, impulse tries to extract the information from the sources. The fields will display this information in light gray <e.g. Derived(Time)>.
- Process type
- You may select between discrete and continuous process type.
- Signal type
- Select the output signal type of your script (Float, Text, Logic, Integer, ..).
- Signal descriptor
- The signal descriptor describes the signal type in more details (e.g the bit width of a logic vector (default<bits=16>)). See below for more details. But in most case, you will use the standard settings (default<>) - Press CTRL-Space to view content proposals.
- Domain Class/Base
- The domain base is just required if your output signal has a different domain than the source signals. If not, just don't touch these settings.
- Domain Range
- Use this field to set the domain range, so the minimum and maximum value of the domain (e.g. 0 .. 1000 Hz)
Production Configuration
- Member: Select the member name or id/index.
In case of Struct signals, enter the member name or id of the member. In case of Array signals, enter the member name or index of the member.
The id defines the position of the member definition, whereas the index means the position of the value. Only in case of arrays, id and index are equal.
Example with members (id/member name):
- 0: A
- 1: B
- 2: C
Struct
- 0: data; 1: data
- 1: data; 3: data (data index and member id not identical)
- 0: data;
- 0: data; 1: data; 2:data
Array
- 0: data; 1: data; 2:data (data index and member id identical)
- 0: data; 1: data; 2:data
- 0: data; 1: data; 2:data
Signal Handling
- Keep tags: The output samples shall keep the tag information of each input sample.
- Ignore 'None': Ignore 'None' samples of the input signals.
- Hide identical: Check to hide sequence of identical samples (will only write to output signal in case of changed sample value/tag, may not have any effect in case of 'Continuous' process type).
The signal handling flags give the user more control over the output signal generation. If the "Keep tags" is checked, the output samples will get the tag information of each input samples. The "Ignore None" flag let the production ignore 'None' input samples. The "Hide identical" hides the production from generating sequences of identical samples.
Operation
Below you find the operation code for the production.
// iterate
while (iter.hasNext() && !isCanceled()) {
// value
Long current = iter.next();
CompoundValue cvalue = input.compound();
if (cvalue == null)
continue;
// none sample
boolean hasMember = cvalue.hasMember(member);
boolean isNone = cvalue.isNone() || !hasMember;
if (ignoreNone && isNone)
continue;
// member value
Object value = !isNone ? value(cvalue, member, targetWriter) : null;
if (!isNone && value == null) // could not convert
continue;
// tag
boolean tag = keepTags && cvalue != null && cvalue.isTagged();
// check identical
if (!hideIdentical || tag != previousTag || !Utils.equals(value, previousValue)) {
// write
if (isNone)
targetWriter.writeNone(current, tag);
else
targetWriter.writeSample(current, tag, value);
// remember
previousTag = tag;
previousValue = value;
}
}
break;
 32/64bit
32/64bit 32/64bit
32/64bit 32/64bit
32/64bit